As we move into 2023, educators are looking for fresh and innovative ways to decorate their classrooms to enhance the learning experience. Good classroom décor can spark creativity, provide comfort, and make learning spaces more engaging. Below are 20 genius classroom decorating ideas that are sure to inspire both teachers and students.
1. Nature-Inspired Themes: Incorporate elements from nature, like plants, to create a calming environment. Botanical prints and live greenery can help improve air quality and boost students’ mood.
2. Interactive Bulletin Boards: Set up bulletin boards that invite interaction—think touch-and-feel sections, question of the week, or rotating student work displays.
3. Educational Murals: Utilize wall space with murals that have educational content such as maps, historical timelines, or science processes.
4. Flexible Seating Options: Offer a variety of seating arrangements like floor pillows, bean bags, and standing desks to accommodate different learning styles and promote comfort.
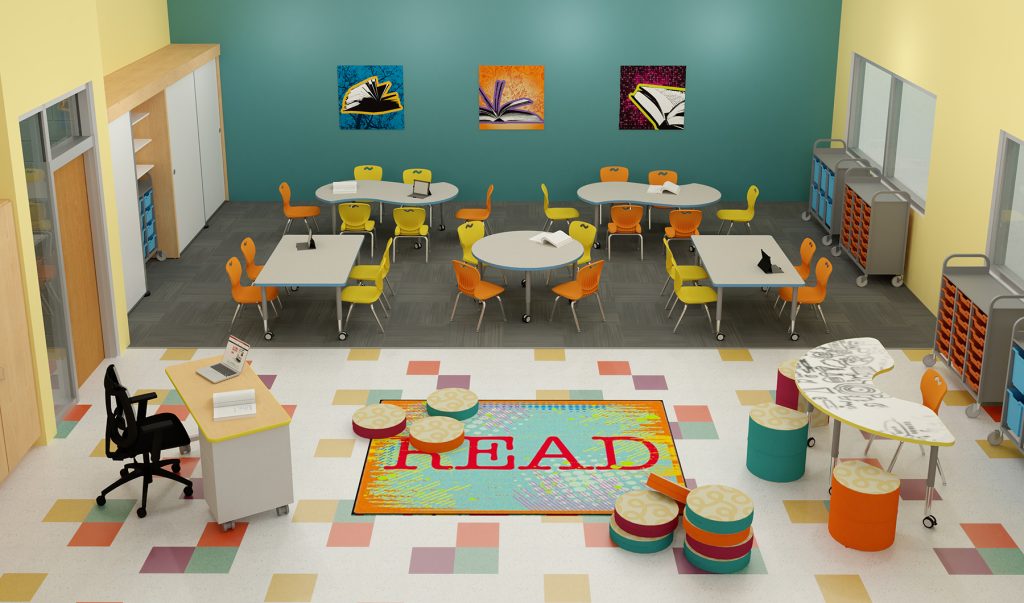
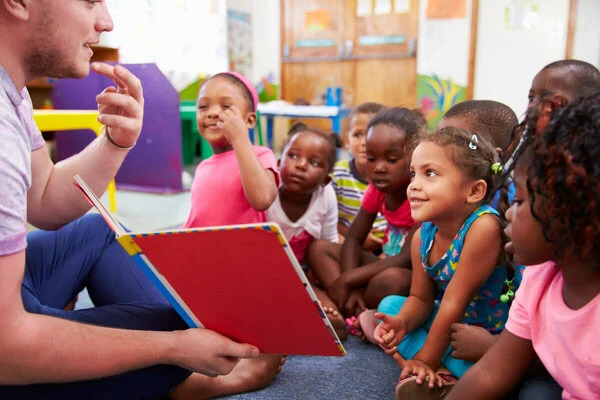
5. Reading Nooks: Carve out a cozy corner of the classroom dedicated to reading, replete with bookshelves and comfy seating options.
6. Color Zones for Learning: Define different areas of the classroom with color themes – blue for calm reading areas, yellow for energetic discussion spaces, etc.
7. Lighting Variety: Introduce different types of lighting—lamps for warm light options and strings of lights for ambient light—to reduce strain from fluorescent overheads.
8. Classroom Themes: Pick a classroom theme that changes annually or by semester – from jungle adventure or outer space exploration to historical eras.
9. Tech-Friendly Spaces: Create specific zones designed for technology use like a podcasting station or a video editing corner equipped with the necessary tools.
10. Class Constitution Wall: Design a space where class rules are visually represented alongside signatures from each student to promote ownership and accountability.
11. Cultural Corner: Dedicate an area to celebrate various cultures represented in your class with artifacts or visual displays providing information about different countries and traditions.
12. Math Manipulative Stations: Set up hands-on math centers with manipulatives that students can use during math workshops or free exploration time.
13. Science Lab Zone: Distinguish part of the classroom as a science lab area where experiments can be conducted safely and materials are efficiently organized.
14. Art Gallery Display: Reserve a wall to display student artwork, providing students with the pride of seeing their creations showcased formally.
15. Inspirational Quotes Gallery: Have a rotating gallery of inspirational quotes related to education and growth mindset accessible for all students to see and read daily.
16. Subject-Specific Decoration Kits: Use removable vinyl decals or thematic kits related to subjects being taught – chemistry concepts, literary figures, historical events etc.
17. Organization Stations: Create clearly labeled storage areas for supplies that encourage self-organization by students such as book bins labeled by genre or math toolkits.
18. World Clock Display: Hang clocks showing different times around the world which can tie into geography lessons and global awareness.
19. Augmented Reality Corners: Incorporate augmented reality posters that come alive through apps on tablets or smartphones offering interactive learning experiences.
20. Sensory Pathways on Floors: Introduce sensory paths made with stickers on floors that guide movement patterns encouraging physical activity breaks throughout lessons.
These genius decorating ideas not only beautify the classroom but also serve educational purposes – from promoting diversity to creating tactile learning experiences – aiming at making the learning environment as enriching as possible in this upcoming year!