Introduction
In the realm of education, few concepts have had as far-reaching an impact as those championed by researchers Paul Black and Dylan Wiliam. Together, they developed a revolutionary approach to education known as “Assessment for Learning,” which seeks to transform the way teachers and students interact with assessments in order to drive better educational outcomes. This article will explore the foundations of this approach, its core principles, and its ongoing significance in education today.
The Origins of Assessment for Learning
The concept of Assessment for Learning (AfL) can be traced back to a seminal 1998 paper written by Paul Black and Dylan Wiliam titled “Inside the Black Box.” In this paper, the two researchers reviewed a vast array of educational studies conducted across different countries, subject areas, and grade levels. The goal of this extensive review was to identify methods that had been proven to be effective in improving student achievement. Across these disparate contexts, Black and Wiliam found one clear commonality: formative assessment was key to driving better learning outcomes.
Core Principles of Assessment for Learning
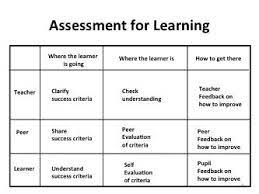
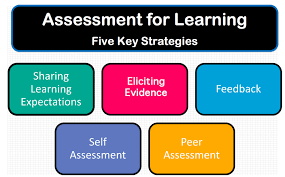
At its heart, AfL is centered around the idea that assessments should not simply function as measures of student performance but should be used as tools to actively enhance learning. This is achieved through several key principles:
1. Effective Feedback: AfL advocates argue that students need timely, specific feedback on their work in order to address gaps in understanding and continue growing. This feedback should be more than simple praise or criticism; it should provide students with actionable guidance on how they can improve.
2. Peer and Self-Assessment: Students are encouraged to engage in self-assessment as a means of becoming more aware of their own strengths and weaknesses. Similarly, involving students in peer assessment processes helps them develop critical thinking skills and foster a collaborative learning environment.
3. Responsive Teaching: Teachers must be attuned to the needs of their students, regularly evaluating what learners comprehend and adjusting instructional strategies accordingly. By responding to student needs in real-time, AfL allows educators to create more personalized and adaptive learning experiences.
4. Formative Questioning: AfL relies heavily on asking meaningful questions that prompt students to think deeply about the subject matter. This process encourages active engagement with the material and helps develop critical thinking skills.
5. Learning Objectives and Success Criteria: Clearly outlining learning goals and objectives helps students understand what is expected of them, while success criteria provide a clear framework for evaluating progress toward those goals.
The Continued Significance of Black, Wiliam, and Assessment for Learning
In the years since Black and Wiliam first outlined their findings on formative assessment and AfL, these principles have continued to shape educational policy and practice around the world. Many school systems now place a high value on professional development that supports effective assessment practices, as well as curricula that prioritize implicit skill-building through ongoing evaluation and feedback.
As education continues to evolve in response to new technological possibilities and social realities, the core principles of AfL offer a guiding framework for educators seeking to empower students in an ever-changing world. Ultimately, the partnership of Black, Wiliam, and Assessment for Learning has made a lasting impact on how we understand teaching, learning, and assessment – carrying powerful implications for generations of students to come.