Introduction:
In today’s world, thinking skills are more important than ever. They play a crucial role in problem-solving, decision-making, and comprehension. Developing these abilities can help individuals adapt to new situations, understand complex concepts, and find innovative solutions to challenges. This article explores different types of thinking skills and provides practical tips for improving them.
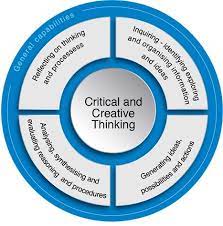
Types of Thinking Skills:
1. Critical Thinking – Critical thinking involves analyzing information objectively and making reasoned judgments based on evidence. It requires the ability to evaluate the credibility of sources, recognize biases, and draw logical conclusions.
2. Creative Thinking – This skill involves generating innovative ideas and finding unique solutions to problems. Creative thinkers are able to see things from multiple perspectives and combine seemingly unrelated ideas in new ways.
3. Analytical Thinking – Analytical thinking involves breaking down complex information or problems into smaller, more manageable parts. This skill is essential for understanding cause-and-effect relationships and predicting future outcomes.
4. Logical Thinking – Logical thinking entails using clear, step-by-step reasoning to reach conclusions based on sound principles and facts. It’s a systematic approach that helps you avoid emotional bias and make well-informed decisions.
5. Reflective Thinking – Reflective thinking involves carefully reviewing past experiences to learn from them and make better choices in the future. It requires self-awareness, open-mindedness, and honestly assessing one’s own strengths and weaknesses.
Tips for Improving Your Thinking Skills:
1. Be Curious – Cultivate your curiosity by asking questions, reading widely, and staying informed about current events or topics that interest you.
2. Practice Active Listening – Focus on understanding what others are saying before responding or forming your own opinion. Active listening helps facilitate empathy, open-mindedness, and a deeper understanding of others’ perspectives.
3. Develop Problem-Solving Strategies – Learn various problem-solving techniques such as brainstorming, mind mapping, and the Six Thinking Hats method. Apply these approaches to everyday challenges to enhance your problem-solving abilities.
4. Engage in Critical Discussions – Participate in debates, enter into thoughtful conversations with others, and learn to appreciate differing viewpoints. Constructive dialogue helps build both critical and reflective thinking skills.
5. Embrace Creativity – Make time for creative outlets like painting, writing, or playing an instrument. These activities help foster creative thinking and inspire innovative problem-solving.
6. Reflect on Your Experiences – Take time to evaluate your decisions and consider how they’ve shaped your life. Learning from past successes and failures can significantly improve your reflective thinking skills.
Conclusion:
Developing strong thinking skills is crucial for success in today’s ever-changing world. By practicing critical, creative, analytical, logical, and reflective thinking, you can become more effective at solving problems, making decisions, and understanding complex concepts. Start by exploring your curiosity, engaging in productive discussions, practicing problem-solving techniques, and reflecting on your experiences regularly to unlock your full cognitive potential.