In the world of mathematics education, place value stands as one of the most critical concepts for students to grasp. It forms the foundation for all higher arithmetic operations and mathematical understanding. Place value teaching resources are tools that educators can employ to effectively impart this fundamental knowledge.
Place value refers to the value of a digit based on its position within a number. Recognizing how the place of a digit changes its value is vital for students as they work with larger numbers and begin performing operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
Teachers have a wide array of place value teaching resources at their disposal. These resources range from physical tools like base-ten blocks and place value charts to digital applications and games that make learning interactive and engaging. Here we’ll explore some effective resources and how they can enrich place value education.
Base-Ten Blocks:
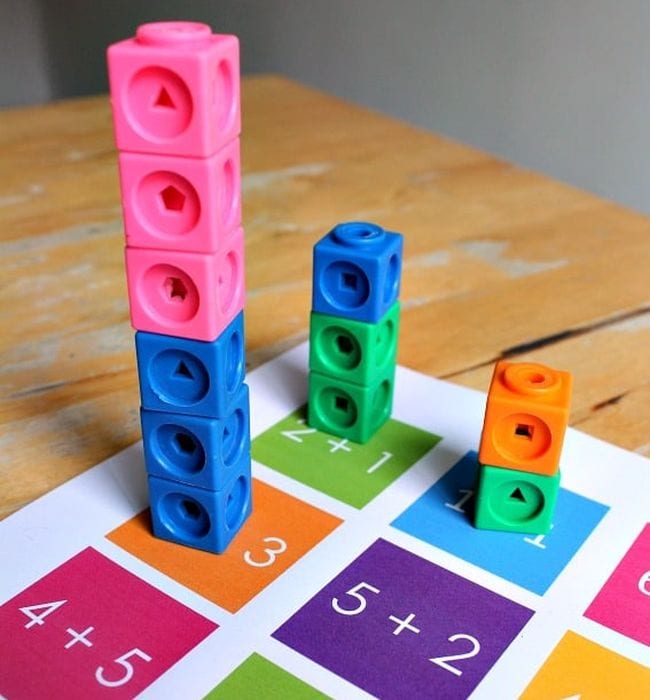
Base-ten blocks are perhaps the most tangible tool for teaching place value. They allow students to build and deconstruct numbers visually and physically. Unit cubes represent ones; rods represent tens; flats represent hundreds; while cubes can be used for thousands, helping students comprehend the magnitude of numbers at each place.
Place Value Charts:
Place value charts provide a visual scaffold for understanding how numbers are structured. They show each place from ones on the right to millions (or beyond) on the left. As students work with these charts, they learn to recognize the significance of zero as a placeholder and how each shift in position alters a digit’s value.
Interactive Whiteboard Activities:
Many classrooms now come equipped with interactive whiteboards, which offer another dynamic avenue for place value instruction. Teachers can create or use pre-made lessons that allow students to drag digits into the correct column, visually breaking down how numbers are constructed.
Online Games and Apps:
Digital games have become increasingly popular for teaching math concepts, including place value. These games often incorporate bright colors, engaging characters, and rewarding systems that motivate students to practice identifying, comparing, and manipulating numbers in their correct places.
Worksheets and Printables:
For more traditional practice, worksheets remain an essential part of teaching. Place value worksheets might include activities where students have to fill in missing numbers on a chart, expand numbers into their component values, or compare numbers based on their digits’ places.
Also crucial is professional development for teachers looking to refine their approach to teaching place value. Many educational organizations provide workshops, seminars, and downloadable guides that offer strategies for making place value instruction more effective.
In conclusion, using diverse teaching resources ensures that all types of learners can access this crucial piece of mathematical understanding. From hands-on manipulatives like base-ten blocks to digital apps that turn learning into play, educators have numerous options at their fingertips for creating a well-rounded approach to teaching place value.