Auto insurance is a fundamental aspect of responsible vehicle ownership, providing financial protection against accidents, theft, and liability. Understanding the intricacies of auto insurance can help you make informed decisions and ensure you have the right coverage for your needs.
The basic components of auto insurance include:
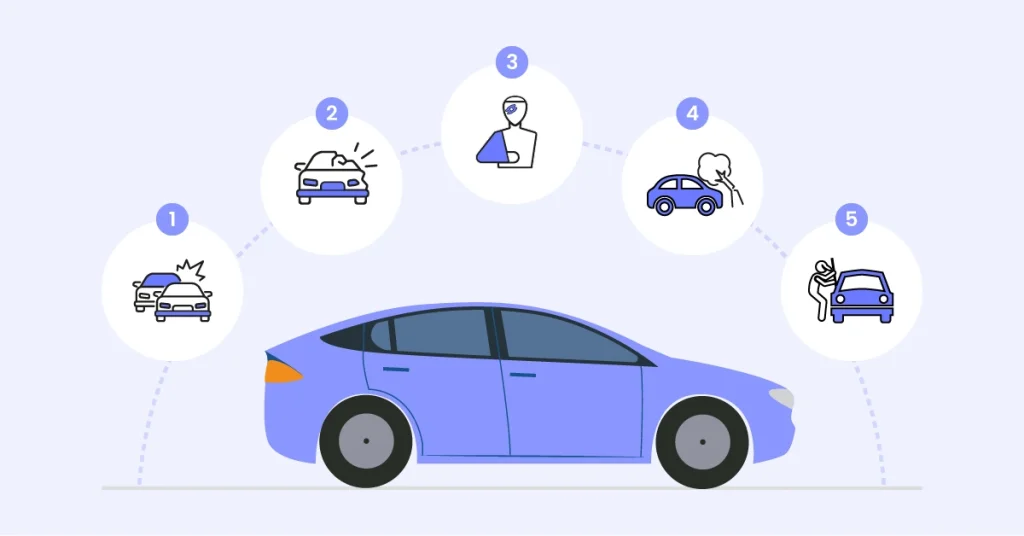
1.Liability Coverage: This is mandatory in most states and covers damages you cause to others in an accident.
2.Collision Coverage: This pays for damage to your vehicle from a collision with another vehicle or object.
3.Comprehensive Coverage: This protects against non-collision incidents like theft, vandalism, or natural disasters.
4.Personal Injury Protection (PIP): This covers medical expenses and lost wages for you and your passengers.
5.Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage: This protects you if you’re in an accident with a driver who has insufficient or no insurance.
When shopping for auto insurance, consider factors such as:
Your vehicle’s make, model, and age
Your driving record and claims history
Your location and typical driving habits
Your budget and desired level of coverage
Many insurers offer discounts for safe driving, multiple policies, good grades (for students), and vehicle safety features. It’s worth asking about these when getting quotes.
One emerging trend in auto insurance is usage-based insurance (UBI) or pay-as-you-drive policies. These use telematics devices to monitor driving habits and can offer lower premiums for safe drivers.
It’s important to review your auto insurance policy regularly, especially after major life changes like moving, getting married, or buying a new vehicle. Your coverage needs may change over time, and staying on top of these changes can ensure you’re adequately protected.
When filing a claim, document everything thoroughly, including photos of damage and police reports if applicable. Understand your policy’s claims process and don’t hesitate to ask questions if anything is unclear.
Remember, while it might be tempting to opt for the minimum required coverage to save money, this can be risky. A serious accident could leave you with significant out-of-pocket expenses if you’re underinsured. Balancing adequate coverage with affordable premiums is key to effective auto insurance management.
By understanding the basics of auto insurance and regularly reviewing your coverage, you can protect yourself financially while enjoying the freedom and convenience of vehicle ownership.