Introduction:
Learning is a complex and dynamic process that goes beyond digesting facts and figures. It involves understanding, interacting, and building relationships with others, as well as developing personal identity and emotional intelligence. In this article, we will examine the significant social and emotional aspects of learning, enabling students to thrive academically, socially, and emotionally.
The Importance of Social Skills in Learning:
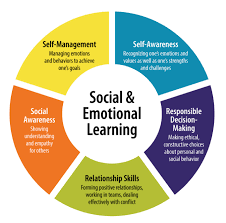
Social skills are essential tools that facilitate academic and non-academic aspects of learning. Students must learn to navigate interpersonal relationships through verbal and non-verbal communication while demonstrating respect and empathy. Collaborative learning activities such as group projects, presentations, and discussions foster an environment for building essential social skills. In turn, these skills contribute to creating a positive classroom atmosphere where students feel connected and motivated to learn.
Emotional Intelligence in Learning:
Emotional intelligence involves recognizing and managing our emotions, a crucial component for achieving success in education. When students understand their emotions better, they can handle stress more effectively by identifying triggers and coping mechanisms. Moreover, they can develop empathy towards other students and engage more empathetically in group work or debates.
Developing Relationship-Building Skills:
Building strong relationships is critical to successful learning experiences. Students must learn how to listen actively, provide constructive feedback and work effectively with others. This helps build trust between peers which provides support during challenges, such as tackling a difficult assignment or overcoming feelings of doubt or anxiety.
Self-Awareness and Self-Regulation:
Having self-awareness means understanding one’s own strengths, weaknesses, values, emotions, and goals. It also involves recognizing personal needs that impact academic performance. By cultivating self-awareness skills through reflection activities or personal assessment tools, students can gain greater insight into their emotional state and learning styles.
Benefits of Strong Social-Emotional Skills in Education:
Developing robust social-emotional skills not only benefits personal wellbeing but also supports academic success. Students who are strong in these areas can more effectively navigate stress, adapt to changing circumstances, and demonstrate resilience in the face of setbacks. They are also more likely to have positive relationships with peers and educators, creating a supportive network that contributes to a healthy learning environment.
Teaching Strategies for Social-Emotional Learning:
To adequately address social and emotional dimensions in the classroom, educators need to be proactive in fostering these skills. Some strategies include:
1. Encouraging students to openly express their feelings and empathizing with their emotions
2. Incorporating collaborative learning experiences
3. Providing opportunities for self-reflection and goal-setting
4. Modeling appropriate social behaviors and emotional responses
5. Creating consistent routines that help students feel secure and engaged
In conclusion, attending to both social and emotional aspects of learning is crucial for personal development and academic success. By integrating social-emotional curricula, educators can create an inclusive classroom environment that cultivates well-rounded individuals ready to tackle challenges with confidence and support from peers and mentors.