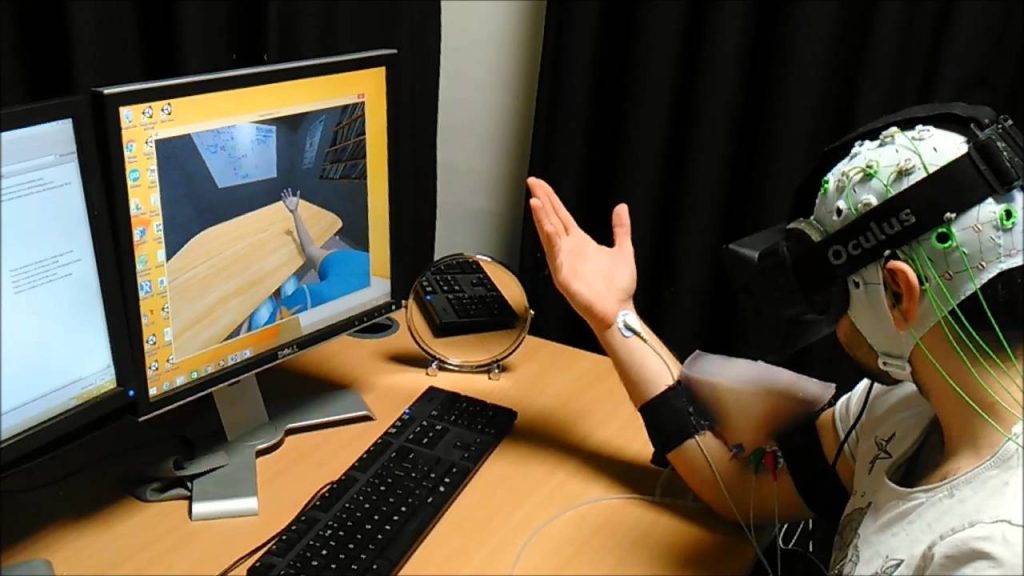
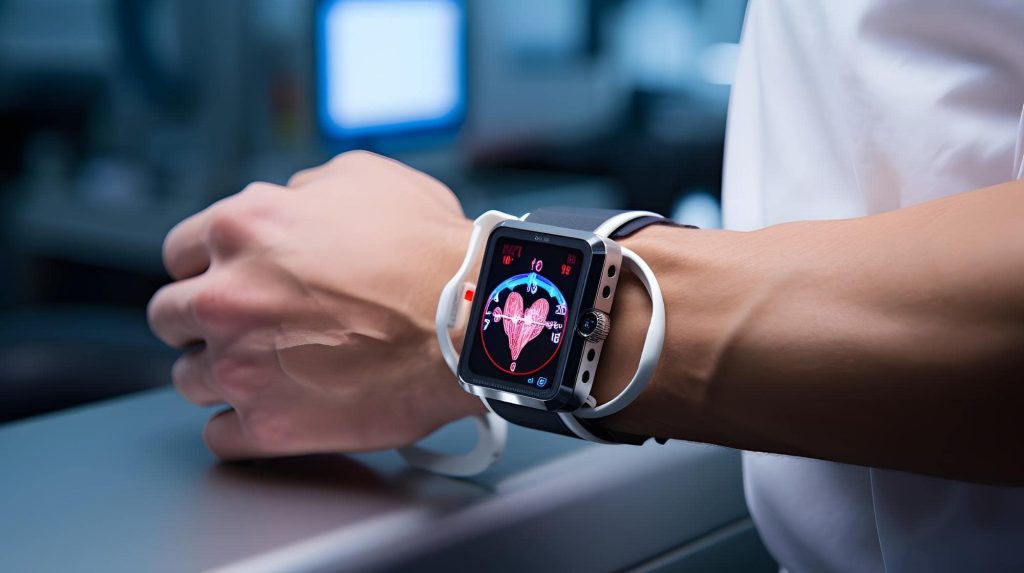
As we approach 2025, wearable technology is revolutionizing the field of behavioral interventions through continuous, real-time monitoring of physiological and behavioral data. These devices, ranging from smartwatches to smart clothing, are providing unprecedented insights into individual behavior patterns and health states.
One of the key trends we’re seeing is the integration of more advanced sensors into wearable devices. Beyond heart rate and step counting, newer devices can monitor everything from sleep patterns and stress levels to blood glucose and even neurological activity. This wealth of data allows for more comprehensive and nuanced behavioral assessments.
As we move towards 2025, we’re seeing the development of AI algorithms that can interpret this complex data in real-time. These algorithms can identify patterns and anomalies that might indicate the onset of a mental health issue or a potential behavioral relapse, allowing for rapid intervention.
Another exciting development is the use of wearables for just-in-time adaptive interventions (JITAIs). These interventions use real-time data to deliver personalized support at the most effective moments. For instance, a wearable might detect rising stress levels and prompt the user to engage in a brief mindfulness exercise.
Wearable technology is also playing a crucial role in sleep interventions. Advanced sleep tracking can provide detailed insights into sleep quality and patterns, allowing for more targeted interventions to improve sleep hygiene and address issues like insomnia.
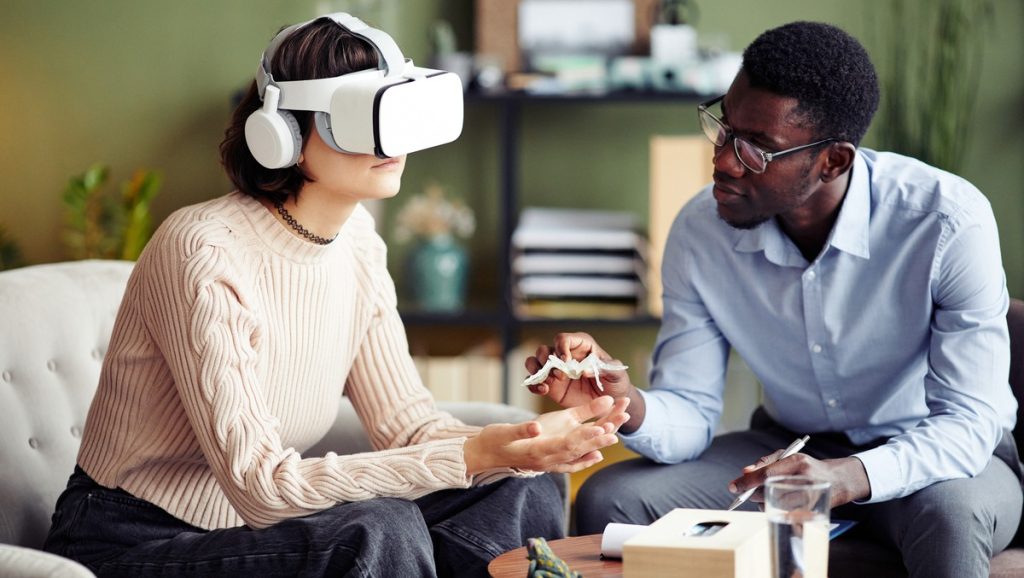
As we approach 2025, we’re seeing increased integration between wearables and other digital health tools. For instance, data from wearables might be used to inform virtual reality therapy sessions or to adjust the difficulty of cognitive training games.
It’s important to note that as wearable technology becomes more prevalent in behavioral interventions, issues of data privacy and user autonomy are paramount. We can expect to see more robust frameworks for ensuring user control over their data and how it’s used.
In conclusion, wearable technology and continuous behavioral monitoring represent a significant leap forward in our ability to understand and influence human behavior. As we move towards 2025, these technologies are set to play an increasingly central role in behavioral interventions, offering the potential for more personalized, timely, and effective support.