Introduction
Performance management and continuous professional development (CPD) are essential aspects of ensuring that employees remain engaged, motivated, and successful. By implementing these strategies within an organization, companies can expect to see improvements in employee retention, increased productivity, and a sense of fulfillment among staff members. In this article, we will delve deeper into the importance of performance management and CPD, their relationship with each other, and practical measures that can be employed to facilitate growth for individuals and organizations alike.
Understanding Performance Management
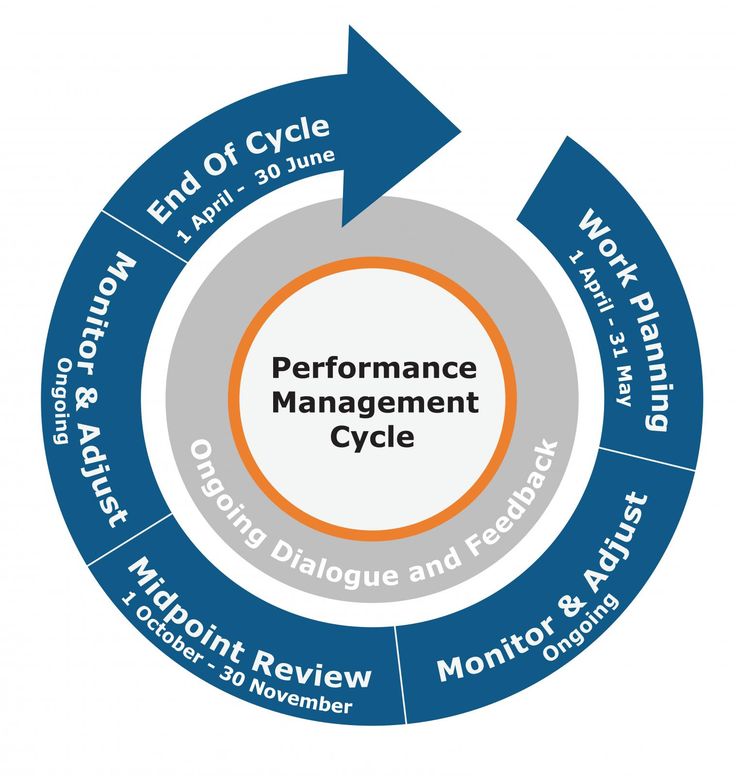
Performance management is a systematic process aimed at ensuring employees are meeting their objectives while also aligning with the company’s broader goals. It involves setting clear expectations for performance, monitoring progress through regular feedback, recognizing achievements or addressing areas for improvement, and ultimately evaluating overall performance against defined criteria.
Regular performance appraisals foster growth by encouraging employees to reflect on their work, identify areas for improvement, and seek new challenges while also motivating them to excel in their roles. Moreover, effective performance management promotes a high-performance culture within the organization.
The Role of Continuous Professional Development (CPD)
CPD refers to the ongoing process of learning and developing skills throughout one’s professional life. The aim of CPD is to ensure that individuals maintain their competence and continually enhance their knowledge and expertise in their respective fields. This could involve attending seminars or conferences, enrolling in formal courses or degree programs, pursuing certifications or licenses, reading industry-related publications or blogs, participating in networking events or workshops, or undergoing internal training activities.
The Connection Between Performance Management and CPD
Both performance management and CPD play significant roles in the growth and development of employees within an organization. Performance management provides a structured pathway for individuals to excel based on the organization’s needs and goals. In contrast, CPD emphasizes personal development opportunities that will enable employees to stay updated within their industry to perform optimally. By leveraging both approaches, organizations can create a workforce equipped with the necessary skills and motivation to thrive in a dynamic business environment.
Practical Measures for Implementation
1.Set clear expectations: Employees should have a clear understanding of their roles, responsibilities, and performance expectations. This can be achieved through regular communication, setting SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant and Time-bound) goals, and establishing performance metrics.
2.Encourage open dialogue: Foster an environment where employees feel comfortable discussing their performance, sharing feedback, and seeking support in achieving their goals. Regular one-on-one meetings with direct supervisors or managers can facilitate these conversations.
3.Provide opportunities for skill development: Provide employees access to various resources such as training courses or workshops that will enable them to stay current in their field while also honing new skill sets relevant to their role.
4.Recognize achievements and address underperformance: Acknowledge employee accomplishments and encourage continuous improvement via constructive feedback. If any underperformance is identified, address it by providing coaching or additional resources to assist the employee in reaching set goals.
5.Foster a culture of learning: Encourage employees to engage with industry trends and continually seek continuous professional development opportunities in line with organizational objectives.
Conclusion
Performance management and continuous professional development play crucial roles in fostering employee growth and maintaining a competitive edge within the business environment. By actively engaging in both strategies, organizations can establish a foundation for continued success while also promoting employee satisfaction and retention.